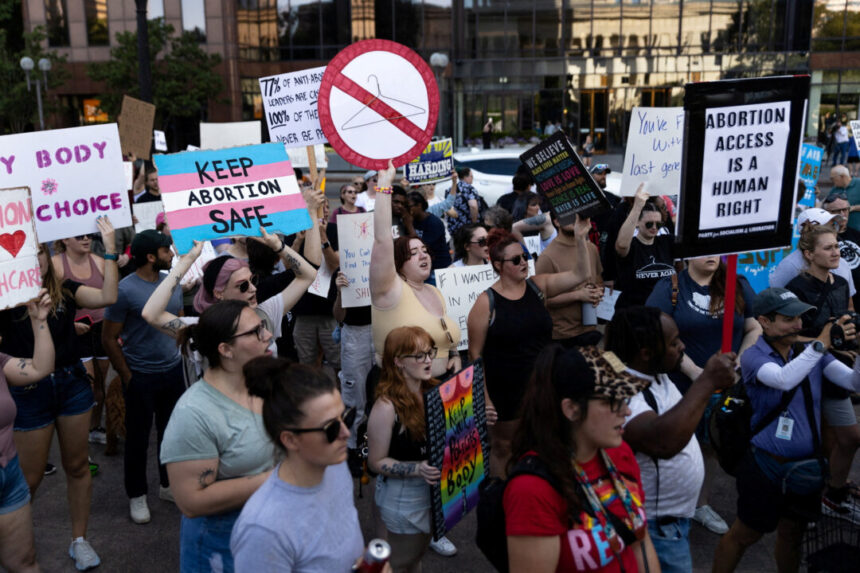The Ohio abortion ban, which prohibited abortions after a fetal heartbeat was detected, has been overturned. This decision came after a judge ruled that a constitutional amendment passed by voters now protects the right to abortion in Ohio. The 2019 law required doctors to determine if a fetus had a heartbeat, usually detectable after about six weeks, and banned abortions if a heartbeat was present unless deemed necessary to prevent the woman’s death or serious health risks. Violations of the law could result in imprisonment. However, a federal court blocked the law shortly after it was enacted, citing U.S. Supreme Court precedent, including Roe v. Wade. The law was permanently struck down in 2023 after the Ohio Supreme Court ruled that it conflicted with the state’s Constitution, particularly the Reproductive Rights Amendment, which guarantees individuals the right to make their own reproductive decisions, including abortion. State officials and plaintiffs agreed that the ban on abortions after a heartbeat was detected should not be enforced. The law, known as S.B. 23 or the Human Rights and Heartbeat Protection Act, contained other provisions, such as making it a felony to perform an abortion without checking for a heartbeat. Ultimately, the court sided with the plaintiffs, stating that any regulation that interferes with the right to pre-viability abortion in Ohio violates the Reproductive Rights Amendment. This ruling has been hailed as a significant victory for reproductive rights in Ohio.
Search
Have an existing account?
Sign In
© 2022 Foxiz News Network. Ruby Design Company. All Rights Reserved.